Shapes names are more than just labels; they are fundamental concepts that help us understand the world around us. From the simple circle to the complex dodecahedron, shapes are integral to mathematics, art, architecture, and everyday life. This article will delve into the various types of shapes, their properties, and their significance in various fields. With a focus on shapes names, we aim to provide you with a thorough understanding that caters to both educational and practical needs.
The study of shapes is not limited to geometry; it extends to several disciplines, including physics, engineering, and design. Recognizing shapes and their names is essential for students, professionals, and anyone interested in visual literacy. In this guide, we will explore different categories of shapes, their characteristics, and applications, along with interesting facts and examples to enhance your understanding.
Whether you are a student looking to improve your knowledge or a professional seeking to apply these concepts practically, this article will serve as a valuable resource. We will provide clear definitions, relevant examples, and visual aids to make the information accessible and engaging. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of shapes names!
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Shapes
Shapes are defined as the external form, outline, or appearance of an object. Understanding shapes names is crucial for various reasons, including enhancing spatial awareness and improving problem-solving skills. In this section, we will discuss what shapes are, their basic classifications, and the role they play in human cognition.
1.1 What Are Shapes?
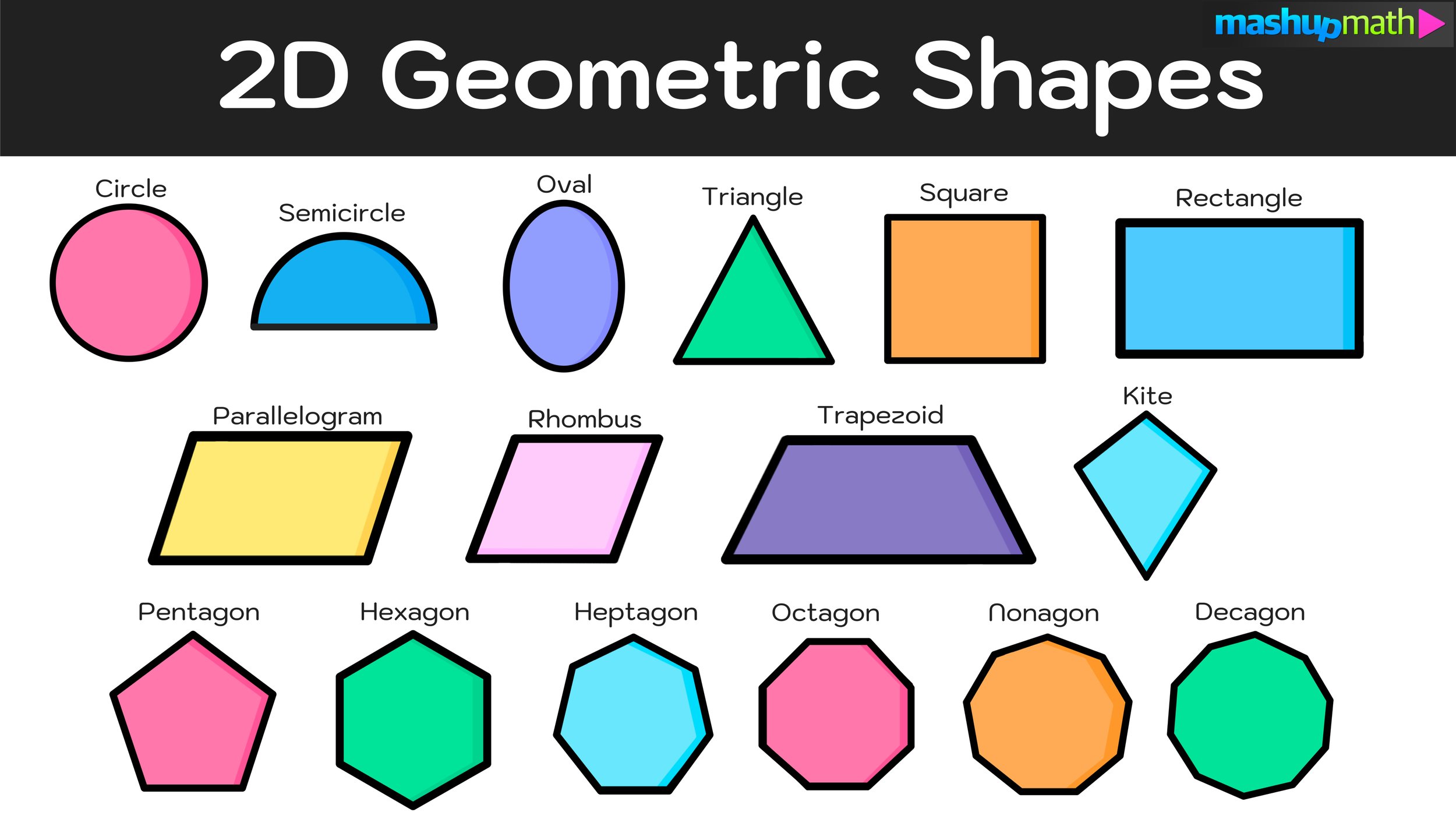
Shapes can be classified into two main categories: two-dimensional (2D) shapes and three-dimensional (3D) shapes. 2D shapes have only length and width, while 3D shapes have depth in addition to length and width.
1.2 Basic Classifications of Shapes
- Two-Dimensional Shapes: These include circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles.
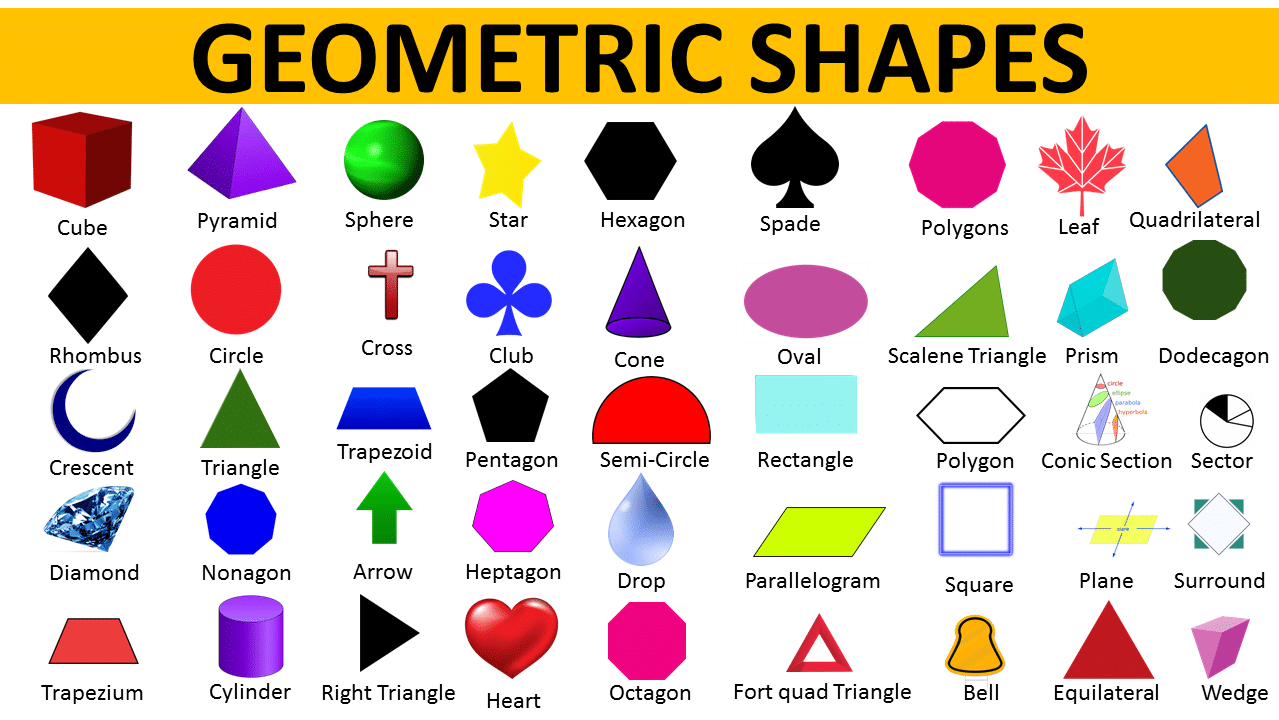
- Three-Dimensional Shapes: Examples include cubes, spheres, cones, and cylinders.
2. Types of Shapes
There are countless shapes in our environment, each with unique names and properties. Below, we categorize and describe the most common types of shapes.
2.1 Geometric Shapes
Geometric shapes are defined by specific mathematical properties and can be categorized into regular and irregular shapes.
- Regular Shapes: Shapes with equal sides and angles, such as equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Shapes: Shapes that do not have equal sides or angles, such as scalene triangles and trapezoids.
2.2 Organic Shapes
Organic shapes are free-form and often found in nature. They are characterized by curves and irregularities. Examples include the shapes of leaves, flowers, and human figures.
3. Properties of Shapes
Each shape has distinct properties that define its characteristics. Understanding these properties is essential for identifying and using shapes effectively.
3.1 Area and Perimeter
The area is the space within a shape, while the perimeter is the distance around it. For example:
- Square: Area = side × side; Perimeter = 4 × side
- Circle: Area = π × radius²; Perimeter (Circumference) = 2 × π × radius
3.2 Angles and Sides
The number of sides and angles also defines shapes. For instance:
- Triangle: 3 sides, 3 angles
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides, 4 angles (e.g., squares, rectangles)
4. The Importance of Shapes in Daily Life
Shapes play a vital role in our daily lives, from architecture to product design. Understanding shapes names can enhance our appreciation of the environment and improve our problem-solving skills.
4.1 Shapes in Architecture
Architectural designs often rely on various shapes to create functional and aesthetic structures. For example:
- Rectangular buildings for practicality
- Circular designs for unique aesthetics, such as domes
4.2 Shapes in Technology
Shapes are also significant in technology, particularly in product design. Designers must consider shapes to ensure functionality and user-friendliness.
5. Shapes in Mathematics
Shapes are fundamental in mathematics, particularly in geometry. Understanding shapes names and their properties is essential for solving mathematical problems.
5.1 Geometric Theorems
Numerous theorems in geometry revolve around shapes, such as the Pythagorean theorem, which relates to right-angled triangles.
5.2 Shape Transformation
Shapes can undergo transformations, including translation, rotation, and reflection, which are crucial concepts in mathematics.
6. Shapes in Art and Design
Artists and designers utilize shapes to convey messages and evoke emotions. Understanding shapes names can enhance creativity and expression.
6.1 The Role of Shapes in Art
Shapes contribute to the overall composition and balance in art. Artists use shapes to direct the viewer's attention and create visual interest.
6.2 Shapes in Graphic Design
Graphic designers use shapes to create logos, layouts, and illustrations. Recognizing shapes and their meanings can improve design effectiveness.
7. Interesting Facts about Shapes
Shapes have fascinating characteristics and significance that might surprise you. Here are a few interesting facts:
- The hexagon is the most efficient shape for tiling a surface.
- In nature, many organisms exhibit fractal shapes, which repeat patterns at different scales.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding shapes names and their properties enriches our knowledge and appreciation of the world. Shapes are not only crucial in mathematics and science but also play a significant role in our daily lives, art, and technology. We encourage you to explore further and engage with this fascinating topic. If you have any thoughts or experiences related to shapes, feel free to leave a comment below!
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has been informative and inspires you to learn more about the wonderful world of shapes. Don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights and information!
Article Recommendations

ncG1vNJzZmilqZu8rbXAZ5qopV%2Bftq652HBmrKCRpbK0ec2apJ6rXp3Brrg%3D