Sea basins are essential components of Earth's hydrosphere, playing critical roles in climate regulation, biodiversity, and human activities. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of sea basins, exploring their definitions, types, significance, and the challenges they face. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about marine geography, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the world of sea basins.
Sea basins, often referred to as ocean basins, are large depressions on the Earth's surface that hold oceanic water. These basins are not just simple containers for water; they are dynamic systems that influence global weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and even human economies. Understanding sea basins is crucial for effective marine conservation and sustainable resource management.
In the following sections, we will discuss the various types of sea basins, their geological formations, and the ecological significance they hold. We will also address the environmental challenges faced by sea basins and the importance of their preservation for future generations.
Table of Contents
1. Definition of Sea Basins
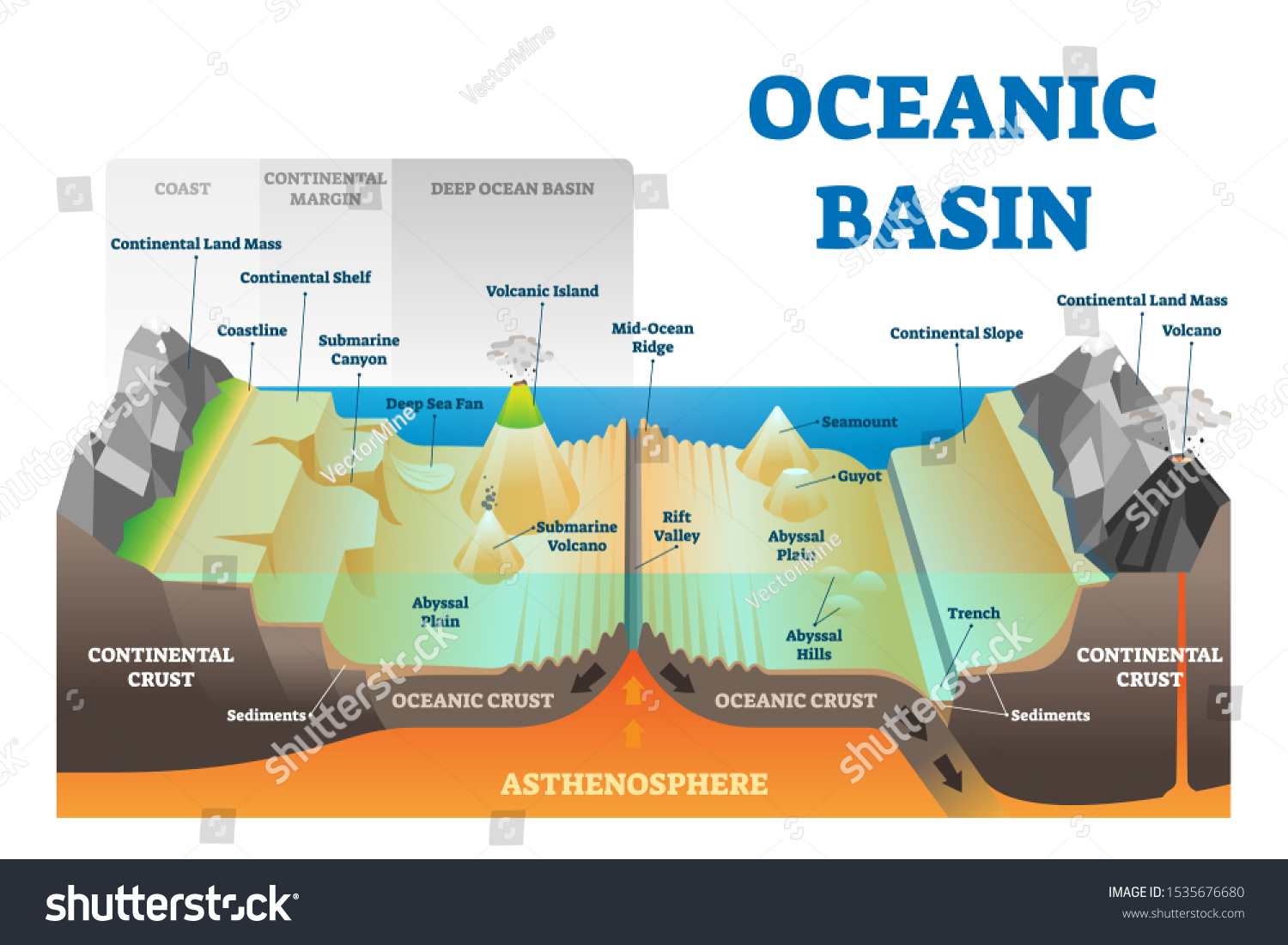
Sea basins are defined as vast, underwater depressions that contain ocean water. They are the largest geological features on Earth, encompassing all the oceans and seas, and are characterized by their depth, area, and surrounding landforms. The primary function of sea basins is to hold water, but they also serve as mechanisms for various geological and oceanographic processes.
2. Types of Sea Basins
There are several types of sea basins, each with unique characteristics. Some of the most notable ones include:
- Marginal Basins: These are semi-enclosed bodies of water located near continental margins, such as the Mediterranean Sea.
- Back-Arc Basins: These are formed behind volcanic arcs and are often associated with subduction zones.
- Rift Basins: These basins occur in regions where tectonic plates are diverging, leading to the formation of new oceanic crust.
- Intracontinental Basins: These are found within continental plates, such as the Caspian Sea.
3. Geological Formation of Sea Basins
The formation of sea basins is a complex geological process that can take millions of years. There are several mechanisms through which sea basins are formed, including:
3.1 Tectonic Activity
Tectonic plate movements are the primary driving force behind the formation of sea basins. When tectonic plates diverge, they create rifts that can lead to the formation of new oceanic crust.
3.2 Erosion and Sedimentation
Over time, erosion from rivers and other natural processes can lead to sediment buildup in certain areas, gradually forming basins.
4. Ecological Importance of Sea Basins
Sea basins are not only vital for holding water but also play a crucial role in marine biodiversity. They serve as habitats for countless species of fish, mammals, and plants. The unique ecosystems within these basins contribute to global biodiversity and are essential for various life forms.
- Habitat Diversity: Sea basins provide diverse habitats, from coral reefs to deep-sea trenches.
- Climate Regulation: The oceans help regulate Earth's climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and heat.
- Resource Availability: Sea basins are rich in resources such as fish, oil, and minerals.
5. Environmental Challenges Faced by Sea Basins
Despite their importance, sea basins face numerous environmental challenges, including:
- Pollution: Industrial waste, plastic debris, and agricultural runoff contaminate ocean waters.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and ocean acidification pose significant threats to marine ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices are depleting fish populations and disrupting marine food chains.
6. Conservation Efforts for Sea Basins
To address the challenges faced by sea basins, various conservation efforts are underway, including:
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Designating specific areas as protected zones to conserve marine biodiversity.
- Pollution Control Initiatives: Implementing regulations to reduce waste and pollution entering the oceans.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating communities about the importance of ocean conservation and sustainable practices.
7. The Future of Sea Basins
The future of sea basins is closely tied to global efforts in climate change mitigation and marine conservation. As we continue to study and understand these vital ecosystems, it is crucial to advocate for their protection to ensure their health and sustainability for future generations.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, sea basins are fundamental to Earth's ecological balance and human well-being. Their importance cannot be overstated, as they support diverse ecosystems, regulate climate, and provide essential resources. As we face increasing environmental challenges, it is imperative to take action to protect and conserve these valuable marine environments. We encourage readers to engage in discussions about ocean conservation and share this article to raise awareness about the significance of sea basins.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative. Feel free to leave your comments below and explore more articles on our site for further insights into marine ecology and environmental science.
Article Recommendations


ncG1vNJzZmilqZu8rbXAZ5qopV%2BcrrOwxKdoaWejmq5ursCsoKdmmKm6rQ%3D%3D