When it comes to measuring speed, the figure of 300 km an hour may seem astonishingly fast. However, understanding what this speed means in practical terms can help contextualize its implications in various scenarios, such as transportation, sports, and even safety. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of speed, specifically focusing on what it means to travel at 300 kilometers per hour, exploring its applications and relevance in our daily lives.
Speed is a fundamental concept in physics and everyday life, influencing how we travel, commute, and interact with the world around us. As we dissect the significance of 300 km/h, we will explore how this speed compares to other common velocities, its impact on transportation methods, and the potential risks and benefits associated with high-speed travel.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the mysteries of speed, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how fast 300 km an hour truly is and what it entails in various contexts.
Table of Contents
Understanding Speed
Speed is defined as the distance traveled per unit of time. In the metric system, speed can be measured in kilometers per hour (km/h) or meters per second (m/s). To understand how fast 300 km/h is, it is essential to grasp the basic principles of speed measurement and its relevance in our daily lives.
Basic Formula of Speed
The basic formula to calculate speed is:
- Speed (v) = Distance (d) / Time (t)
Using this formula, a speed of 300 km/h means that a vehicle travels 300 kilometers in one hour.
300 km/h in Context
To put 300 km/h into perspective, consider the following scenarios:
- A commercial airplane typically flies at speeds between 800 to 900 km/h.
- A high-speed train, such as the Shinkansen in Japan, can reach speeds of up to 320 km/h.
- Sports cars, like the Bugatti Chiron, can achieve speeds exceeding 400 km/h.
Traveling at 300 km/h is significantly faster than typical highway speeds, which usually range from 100 to 130 km/h in most countries.
Comparative Speeds
To better understand how fast 300 km/h is, let’s compare it to other speeds:
- Walking speed: approximately 5 km/h
- Average cycling speed: around 15-25 km/h
- City driving speed limits: often 50-80 km/h
Clearly, 300 km/h far exceeds these common speeds, illustrating the extraordinary nature of such velocity.
Transportation Methods at 300 km/h
Various modes of transportation can achieve speeds around 300 km/h:
- High-Speed Trains: Some of the fastest trains in the world, such as the French TGV and the Japanese Shinkansen, can travel at or near this speed.
- Supercars: Luxury sports cars designed for high performance are engineered to achieve speeds close to, if not exceeding, 300 km/h.
- Aircraft: While commercial jets fly faster, private jets are often capable of cruising at speeds ranging from 300 to 600 km/h.
Safety Implications of High-Speed Travel
Traveling at high speeds comes with inherent risks. Here are some safety considerations:
- Increased Stopping Distance: At 300 km/h, the distance required to stop a vehicle is substantially greater than at lower speeds.
- Reaction Time: Higher speeds reduce the time available for drivers to react to hazards.
- Impact Severity: Accidents occurring at high speeds result in more severe injuries and damage.
Technological Advancements Supporting High Speeds
Advancements in technology have enabled vehicles to achieve such remarkable speeds:
- Aerodynamics: The design of vehicles has improved, reducing drag and allowing for higher speeds.
- Engine Technology: Innovations in engine design and fuel efficiency have made high-speed travel more achievable.
- Safety Features: Modern vehicles are equipped with advanced safety technologies that help mitigate risks associated with high-speed travel.
Real-World Examples of 300 km/h Travel
Real-world applications of speeds around 300 km/h include:
- High-Speed Rail: Countries like France, Japan, and China have successfully integrated high-speed rail networks that operate at these velocities.
- Motorsport: In racing, vehicles often reach speeds exceeding 300 km/h, showcasing the capabilities of modern engineering.
- Aviation: Certain private jets and military aircraft can cruise at speeds around 300 km/h.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how fast 300 km/h is provides valuable insights into the world of speed and its implications. Whether in transportation, sports, or aviation, speeds of this magnitude challenge our perception and highlight the advancements we have made in engineering and technology. As we continue to evolve in our ability to travel faster, it is crucial to consider the safety and practical aspects of high-speed travel. We invite you to share your thoughts on speed and its impact on your life in the comments below!
Thank you for taking the time to explore this fascinating topic with us. We hope to see you back here for more insightful articles in the future!
Article Recommendations
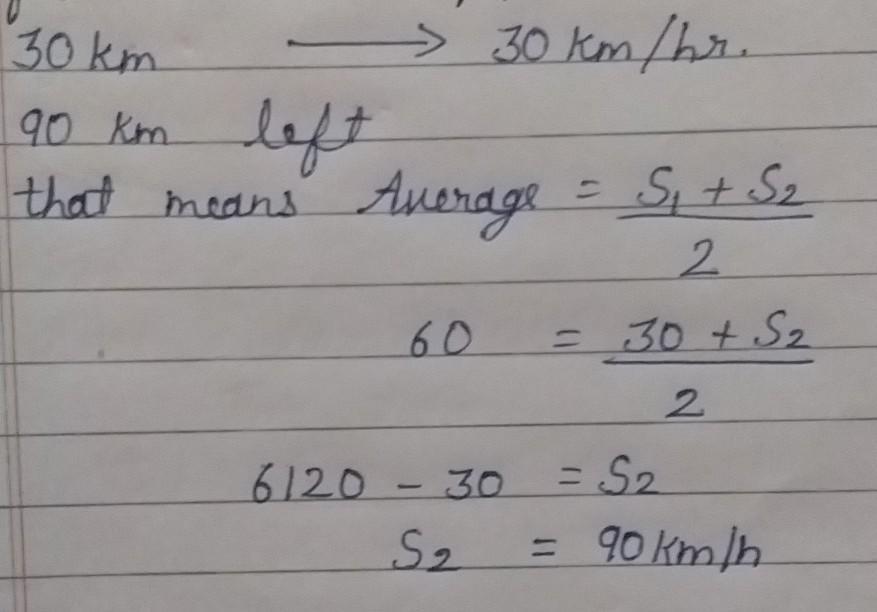


ncG1vNJzZmilqZu8rbXAZ5qopV%2BcrrOwxKdvaKCfrHqnrdKtZKKrXWh9cXnKpmSapl2dvLa%2BjaGrpqQ%3D